Creating virtual environment in Python is quite important thing to know if you are venturing to the world of Python Programming.
Virtual Environment in Python may sound complicated at first if you haven't played around it.
Let's delve into it. Why do we need a virtual environment? When we can just installed Python directly to the system.
One good thing for creating Python virtual environment, is you can have multiple environments on Python on your system and also different versions.
If 2 or 3 people are using the same server or computer, it won't be ideal that each person will use same environment and mess up the work of the other person.
And also if your coding is good for a specific version of Python, the syntax may not work on new versions of Python and this is where virtual environment comes into the scenario.
How do we create a virtual environment in Python?
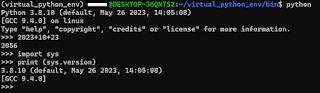
It's quite straight forward, here's the command. Of course this assumes that Python has been installed and ready to be use in your system.
python3 -m venv /home/your-name/whatever_name_of_the_virtual_python_env
The path is not restricted to your home directory it could be in /usr/local/bin or anywhere in your Linux environment.
Screenshot below shows how to create a virtual Python environment.
Right after creating the virtual environment, you can use the "cd" or change directory command and access the newly created virtual environment.
Screenshot below shows the contents of the virtual environment.
Find the "bin" folder, cd to the bin folder and on this folder you can find the "activate" command.
By using the "activate" command, it would mean that the specific folder or path to the Python virtual environment is the currently active Python environment. Of course, the "deactivate" command is the way to disable or deactivate the current environment.
Stay safe! and Keep things up!
Do ASAP, Always Say A Prayer...
Practice O.T.G. = Obedience To God
Make time for Prayer and Meditation.
Take time to kneel down and Pray!
================================
Free Android Apps:
Click links below to find out more:
Free Android Apps:
Click links below to find out more:
Excel Keyboard guide:
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=chrisjoms.myexcelapplicationguide
Heaven's Dew Fall Prayer app for Android :
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=soulrefresh.beautiful.prayer
Catholic Rosary Guide for Android:
Pray the Rosary every day, countless blessings will be showered upon your life if you recite the Rosary faithfully.
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.myrosaryapp
Divine Mercy Chaplet Guide (A Powerful prayer) BFF = Be Filled Faith:


Comments
Post a Comment